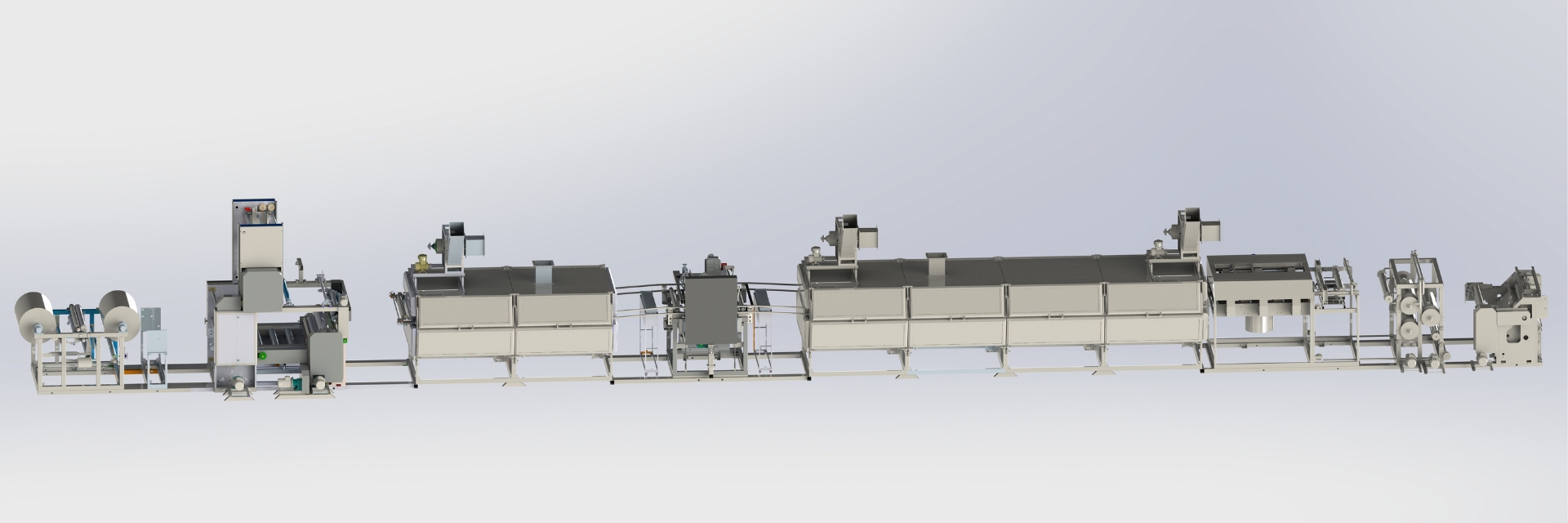
A High-Speed Paper Impregnation Line is an advanced industrial system designed for the efficient treatment of paper with resin solutions, commonly used in the production of decorative laminates, pre-laminated boards, and other engineered surfaces. These lines are engineered to ensure uniform resin impregnation, optimal drying, and smooth operation at high speeds, meeting the demands of modern manufacturing processes.
Key Features:
- High-Speed Operation: Designed for continuous, high-capacity production, ensuring efficiency and scalability.
- Resin Application Systems: Precise application of phenolic, melamine, or other resin types for consistent quality.
- Advanced Drying Ovens: Multi-zone drying technology for uniform curing and controlled moisture content.
- Customizable Line Configurations: Tailored solutions to meet specific production requirements, including variations in paper width and resin type.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporates energy-saving technologies for reduced operational costs.
- User-Friendly Interface: Automated control systems for real-time monitoring and easy operation.
Applications:
- Decorative laminates (HPL/CPL)
- Pre-laminated particleboards and MDF
- Edge bands and compact laminates
Key Features and Process Overview:
- Paper Feeding System:
- Unwinding: Large rolls of kraft paper are unwound and fed into the impregnation system. The paper must be properly tensioned to avoid tearing during the process.
- Precision Feeding: Ambica Industries would provide a feeding system that ensures the smooth, even delivery of the paper to the impregnation unit.
- Impregnation Process:
- Chemical Bath or Roller Coating: The kraft paper passes through a chemical bath or is coated by rollers that apply an impregnation solution. This solution could be:
- Resins: For enhancing the strength, water resistance, or heat resistance.
- Wax: For water-proofing properties.
- Fire Retardants: For making the paper more resistant to fire.
- Plasticizers: To increase flexibility.
- Other Chemicals: Depending on the desired application, the impregnation could include other chemicals for specialized applications, such as anti-bacterial agents, UV inhibitors, or colorants.
- Chemical Bath or Roller Coating: The kraft paper passes through a chemical bath or is coated by rollers that apply an impregnation solution. This solution could be:
- Drying Section:
- After the paper has been impregnated with the solution, it passes through a drying oven or air-drying system to remove excess moisture or solvent. This step is critical to set the impregnation and ensure the paper retains its desired properties.
- Heat Control: The drying section would be designed to maintain precise temperature and airflow to avoid damaging the paper.
- Curing Process (Optional):
- If resins or certain chemicals are used, a curing oven may be included in the system to complete the polymerization process. This step ensures the resin hardens and bonds effectively with the kraft paper.
- Cooling System:
- After drying or curing, the impregnated kraft paper is cooled to stabilize its properties. A cooling section ensures that the paper does not become too soft or lose its rigidity.
- Cutting or Slitting:
- The impregnated kraft paper is cut into the desired dimensions (sheets or rolls), depending on the final product specifications. Automated slitting machines can be used for high precision.
- Packaging:
- Once the paper is impregnated and processed, it is packaged in rolls or sheets and is ready for shipment to customers.